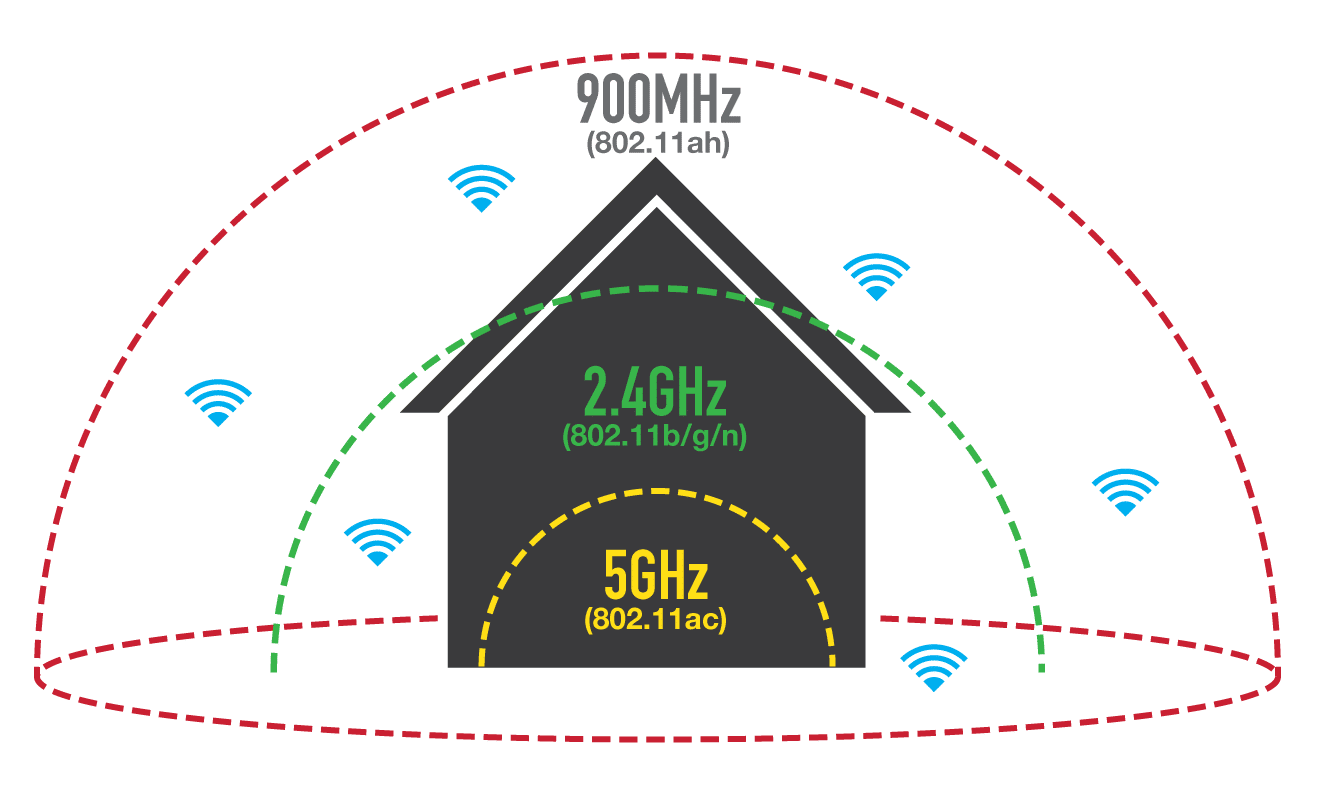
The emerging low power IEEE 802.11ah Wi-Fi standard will face a number of challenges as it seeks to address the limitations of existing 802.11 technologies for large-scale wireless sensor networking, Internet of Things (IoT) and machine-to-machine (M2M) applications in terms of both energy consumption and coverage. In ABI Research’s latest report, Market Opportunities for Low Power Wi-Fi and 802.11ah, it finds that annual IC shipments are set to reach just 11 million units by 2020, four years after the appearance of the first chipsets expected in 2016.
Operating in the sub-1 GHz (S1G) license-exempt bands, 802.11ah offers a much greater range over 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz technologies, while several further enhancements have also been made to the PHY and MAC layers, such as power-saving mechanisms to support several years of battery life, support for up to 8,191 devices per access point, and an extended range mode offering 150 kbps of throughput at a distance of 1 km. These enhancements make it attractive to IoT markets such as the smart home, healthcare and fitness devices, and automation and control.
The standard will find itself competing in the increasingly crowded and fragmented IoT connectivity space, while the move to the S1G spectrum brings new challenges such as incompatibility with existing infrastructure. Whereas other Wi-Fi standards, such as 802.11ac, are backwards-compatible with existing 802.11a/b/g/n routers, 802.11ah enabled products will require a separate gateway or new access point with an 802.11ah radio. This puts it in direct competition with other technologies such as ZigBee and Thread.
“The success or failure of 802.11ah will greatly depend on how long device designers and manufacturers are willing to hold back on developing products using alternative technologies and wait for the standard to develop. There are already strong and well-established low-power, low-cost wireless connectivity technologies available on the market, many of which are operating on the globally available unlicensed ISM bands. Tri-band devices supporting Sub-1GHz, 2.4GHz and 5GH will need to come quickly to the market if it is to have any chance of success,” says Andrew Zignani, Research Analyst at ABI Research.
Recent delays in the standards development process will also need to be quickly resolved in order to ensure that the technology, which is already relatively late to the party, has every chance of success. “With Bluetooth and 802.15.4 technologies such as ZigBee and Thread gaining momentum in the smart home and other IoT verticals, it is becoming increasingly clear that any remaining issues will need to be quickly resolved in order to ensure that the window of opportunity for 802.11ah, which is already closing very rapidly, does not slam shut altogether,” continues Zignani.. “Upon its arrival, 802.11ah will find itself behind the latest developments in standalone chipsets, combo ICs, and IoT platforms of competing solutions, and likely at a higher cost.
Source | ABI Research
These findings are part of ABI Research’s Wi-Fi Research Service, which includes research reports, market data, insights, and competitive assessments.