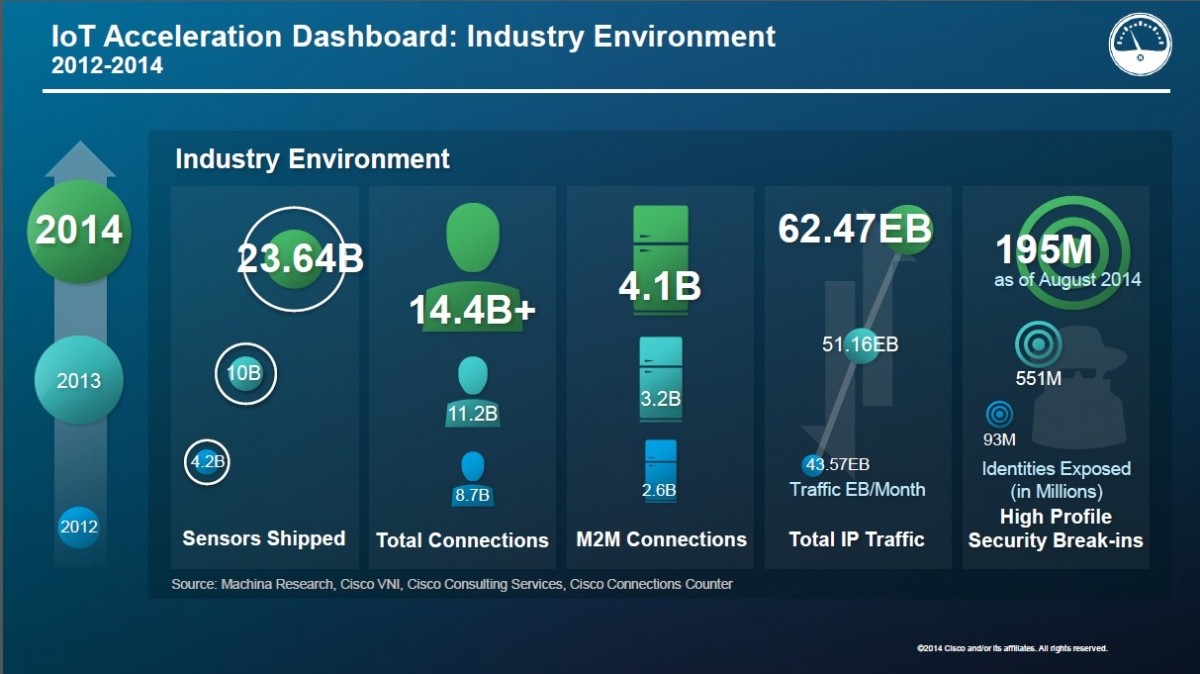
Soon enough, all of us, in our own spheres of work, will probably consume or design – products and services – that have a bit of IoT. But that means we would also need to take informed decisions how IoT fits into what we do. And that calls for a little deeper technical understanding of this overwhelming domain, unfazed by the surrounding sensation.
At the Core
Think of any IoT-based solution, like an intelligent warehouse or smart utilities. At the core of the solution lies a set of specialized devices (including sensors and systems-on-chip) connected to the Internet using a different set of network protocols. Even as we see disruptive innovation on all fronts, there are stabilizing standards, based on early experiments and insights into what works and what doesn’t.
Sensors of IoT
Different types of sensors are being used in different applications – ranging from environmental monitoring to surveillance. Different device characteristics pertaining to size, reliability, power consumption, network connectivity, etc. may be desirable in different usage scenarios. Chip designers and manufactures are actively involved in the IoT ecosystem and are bringing up differentiated products catering to a diverse range of IoT applications.
Wireless Sensor Networks have been in existence for a fairly long time, but newer protocols are being defined to ensure that IoT devices can connect with the existing Internet infrastructure. Newer protocols are being designed both at the network layer as well as the application layer. While network layer protocols like 6LowPAN deal with wireless connectivity between devices and a gateway node to the rest of the application, application layer protocols like CoAP and enable sending across machine-generated messages to the rest of the application.IoT was envisaged to work on top of an IPv6-enabled network which makes for interesting network design considerations.
Security
IoT applications may deal with sensitive data, especially when wearables and personal health monitoring applications are considered.Work is already in progress to define security standards both for data transmitted through the network and data stored in a database.
Constructing Solutions
The scope for designing new solutions based on IoT is simply endless. But knowledge of the emerging technical standards as well as application design principles may help you get there faster.
Designing an IoT Application is an inherently complex exercise. Fortunately, there are architectural patterns that can be emulated – both in terms of application design and application deployment. Most IoT applications connect ‘things’ in our universe to backend systems – that may already exist as part of a larger IT system, or are deployed specifically for an IoT-based solution. The back-end system could be an ERP system running complex business operations, an analytical engine capable of making deductive and predictive inference from huge amount of sensor data, and so on. The fact that IoT has started to trend after Cloud and Big Data has already gone mainstream, creates more options for deploying IoT-based applications. In particular, the ‘things’ could well be connected to a cloud-based backend or analytics platform. An ‘IoT Gateway’is a standard component in most deployments that connect devices to back-end processes – on-premise or on the cloud.
Streamlining services and solutions
Architectural patterns lead to understanding of common services that most IoT applications need. These include device management and monitoring, protocol handling, connectivity to back-end systems, and data analysis. These common services are being built into so-called ‘IoT Platforms’ and offered to IoT application developers. That helps focus on the differentiating solution based on IoT instead of re-inventing infrastructure services.
The field of IoT has synergies with Cloud Computing, Big Data Analytics, and even Data and Application Integration domains, which is manifested by IoT-enabled offerings from vendors specializing in these domains. For IoT developers, this means a large set of building blocks can be leveraged in implementing an IoT-based solution.
The vast domain of IoT is full of intriguing questions, but we are beginning to find answers for many of them.
The report marks the beginning
The Technical Report titled ‘IoT: Devices, Network and Applications – A Technical Report’ published by TechYugadi (techyugadi.com) gives you a good sense of where the technology stands as of today. It is a concise report of around sixty pages, but intended to offer a clear and comprehensive picture on most of the topics described above.
Apart from discussion on technical standards and application architectures, the report brings to you case studies of a few IoT platforms and products, and a few application blue-prints from domains such as home automation and personal health monitoring. This way it gets real! And hopefully helps you cross the chasm from buzzwords to ideas!