The notion of IoT emerged from the earlier work on machine to machine communication or in short M2M. M2M was the beginning to start taking data from devices/sensors and feeding it to internet through M2M gateways, for data processing servers etc. This is known as M2M because there is no human intervention required right from the point of data generations to the point of data processing.
As at time GSMA chief strategy officer Mr Hyunmi Yang, said ““Mobile networks are the platform upon which the M2M industry is being built and mobile operators are at the forefront in shaping the new business models that are driving this exciting market forward,”.
Essentially it was about a network of devices, called ‘capillary network’ connected to ISPs or WAN/MAN through a M2M gateway. The whole enablement of IT is managed through remote connectivity.
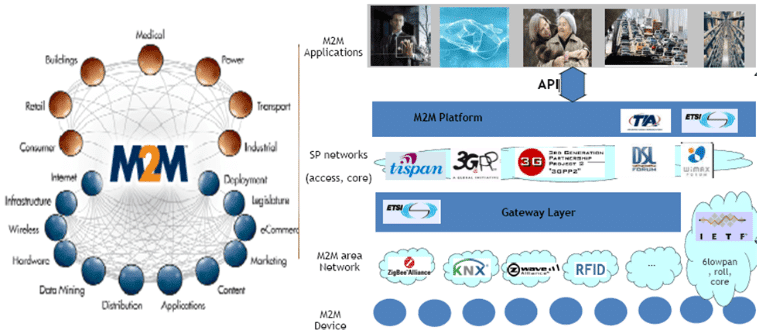
People took it in larger perspective as thought the same concepts about anything which can create or generate data, and transformed it new notion of IOT and also some time referred to as Internet of everything IOE.
IoT means Internet of Things, in literary term it’s like expansion of connectivity to things not only to human’s assistance for remote connectivity that is only ‘Internet’.
There are radios already available for Low range and low power connectivity and also devices and sensors. IoT is for what then – to rejuvenate this industry by creating a buzz in disruptive environment. Definitely not, but it could not be denied that such industry has taken or created much ado around IoT, which is actually not IoT but a kind of Automation only.
Although good to specify some has come with categorization like Industrial IoT or IIoT. There are technologies like BLE, LORA, ZiGBEE, Sigfox, LPWAN, already there and have a significant ecosystem too, and so could be said for devices with sensors – enhanced with LTE backhaul connectivity and miniaturization.
IoT is widely used to create the buzz around, though the term IoT is essentially about global connectivity, much like internet. It’s essentially about connectivity of devices, with zero human interaction, to far reaching data centers. This is possible only with the networks of capacity and capability to connect this massive devices hives. The hives with different kind of requirements like throughput, signaling, and so on.
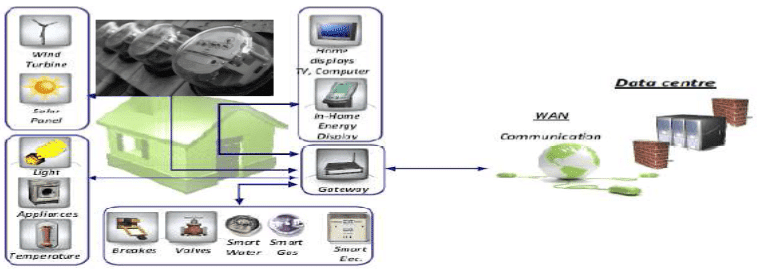
Like taking a smart metering example here.
3GPP has come up with standards on it like LTE-M, NB-IoT and also GSM specific technological tweaks to cater such issues. But there is no big picture across the industry around IoT as a holistic system.
IoT is relevant with big data and analytics, and could help and also be squared up with AI and machine learning.
Meanwhile the GSMA has stated that NB-IoT and LTE-M will both be essential components of 5G in connecting IoT and has urged mobile operators to offer services and products, not just connectivity, if they want to capture some of the $1.1 trillion market opportunity available by 2025.
What’s the 3GPP standards are about for IoT, essentially what they provides, is also known as cellular IoT or in short C-IoT, and here is the way 3GPP portfolio of technologies available for IoT.
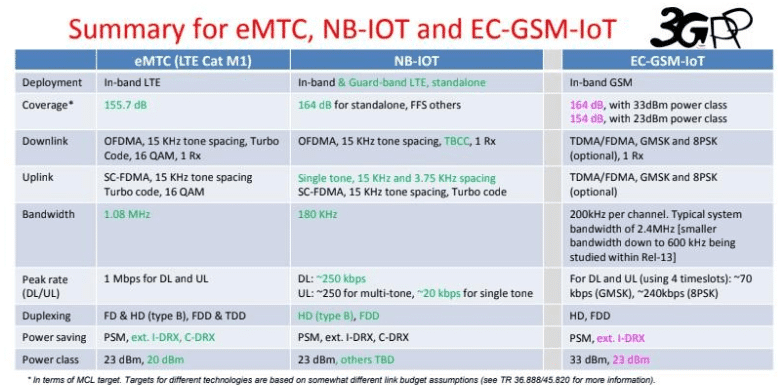
- eMTC: enhanced machine type communication with new power saving mode (PSM) for cat 0 devices. 3GPP started work on this from release 12 onward, the focus is to provide low data and low power devices/sensors for long life sustainability and zero manual touch. Although it goes with LTE services and can cater high data rates but is flexible and focused enough for narrow band uses like for 1.08 MHz.
- NB-IoT: This is about the specific changes in LTE standards, basically finding a tweak around LTE radio frame structure to support IoT data traffic, massive devices/sensors connectivity, widespread coverage, and low cost focus. It support narrow band up to 180 KHz.
NB-IOT works in 3 modes of operations
a. Stand-alone mode, in this mode its use standalone spectrum for IoT services, generally the spectrum used for GSM/GPRS uses.
b. Guard Band, this mode utilized LTE guard band’s unused resources.
c. In-Band, this mode utilized resource from normal LTE carrier, also known as LTE-M.
3. EC-GSM-IoT: This is about using GSM/GPRS technology for IoT devices/sensors connectivity, this also provide power saving mode (PSM) enhancements and enhances GSM security.
This article is written by Saurabh Verma, Founder Director & Chief Technology consultant, Fundarc Communication (xgnlab).