While we cite out smart cars, there is a co-operative systems innovation in Europe which is a part of intelligent mobility systems. The city circuit is a venture of service providers like automotive supply chain, road transport and digital industries engaged in development and testing of vehicles integrated with their environment.
Obstacles
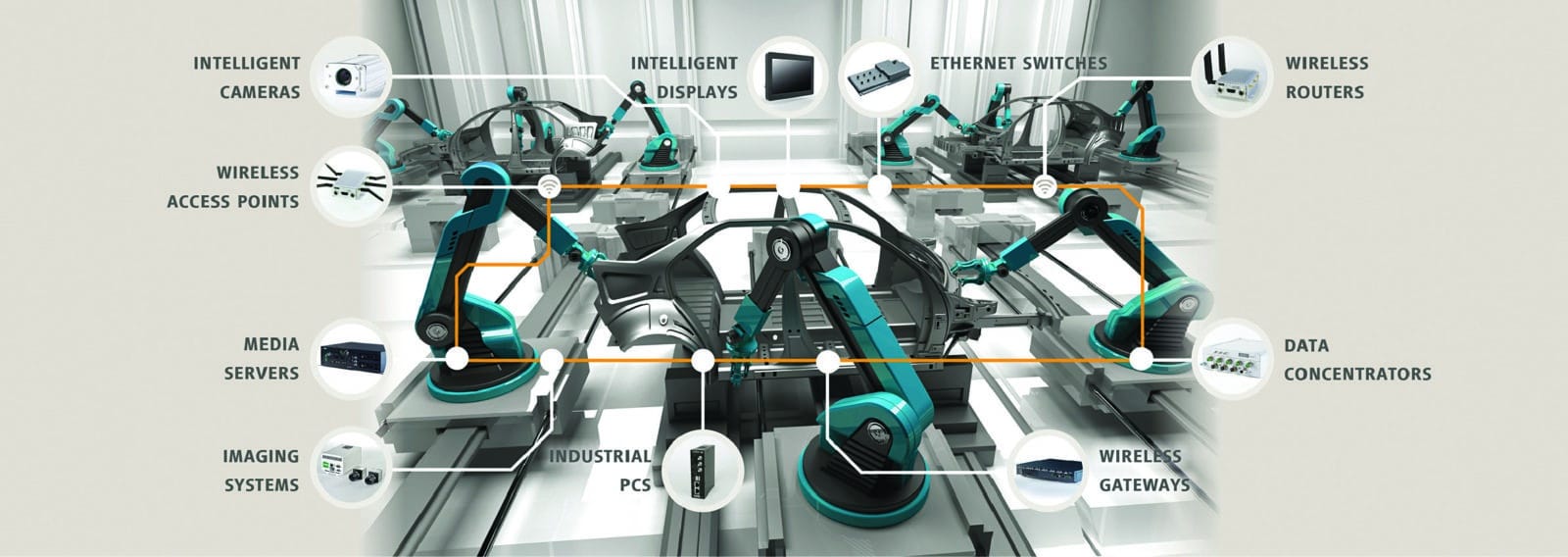
The Deutsche Bank estimates that in industrial-level automation, the level of efficiency, accuracy and reliability achieved with the IIoT increases the productivity by 30 per cent. Still, some industries in India look at the IIoT as a separate business segment where they need to spend money on sophisticated things.
There are other reasons too. In case of critical machinery control, there is a high possibility of failure if timings of the control signals mismatch. So, there needs to be a safe and secured networking system for communication between systems even miles apart.
Moreover, there is a requirement of flexible hardware, software and networking platforms that are capable enough to be in-sync with each other.
With the sophisticated network comes the responsibility of data handling and security. Lots of machinery is required to connect with each other and derive data from functions. Data being very large, it needs to be clubbed in a single cloud-based system. This cloud-based system should be tightly secured so that only registered users can extract the company’s factory automation data.
It is foreseen that by 2020, companies will spend roughly above $1.5 trillion a year on the IIoT. As many as 96 per cent of industrialists expect an increase in the number of attacks on the IIoT in 2017. So leading companies have created some protocols to plan a tightly secured IIoT system. From understanding the concerns to studying the attack trends, from evaluating the risk of blending IT and OT to considering the devices and gateways, some best practices have been initiated by the experts.

Future outlook
Nathan says, “The IoT is making big strides due to new advances on both hardware and software fronts. On the hardware side, printed flexible sensors are the future of technology for the IIoT. These sensors are lightweight and low-cost, which will be a critical evolution for the field. On the software front, edge computing is proving to be a game changer by allowing cloud-based machine learning models to be pushed to distributed machine environment, thereby making hardware more intelligent, fast, and reliable.”
Also, edge computing would be implemented to push intelligence to the edge.
Sensors ranging from optical and temperature to piezoelectric, and gas and humidity sensors will all be printed on flexible substrates, representing a growing market. This is a technology forecast for the period 2017-27, when major players will shrink the size of sensors to increase their number in a unit, thereby increasing the number of functions it can perform. With properties like mechanical flexibility, thinness and weightlessness, flexible sensors are all set to break the barriers of commercialisation.
Edge computing technology has become a common framework that builds an ecosystem for plug-and-play of components in a system through simplification and standardisation. Thus, it makes interoperability between devices, applications and services possible.
Experts envision the future of the IIoT as one which would deal in security solutions for the IIoT and deploy millions of devices connected to each other. We cannot wait any longer for a single concept of the IIoT that would connect millions of devices worldwide, thereby enabling just one organisational culture for all nations.