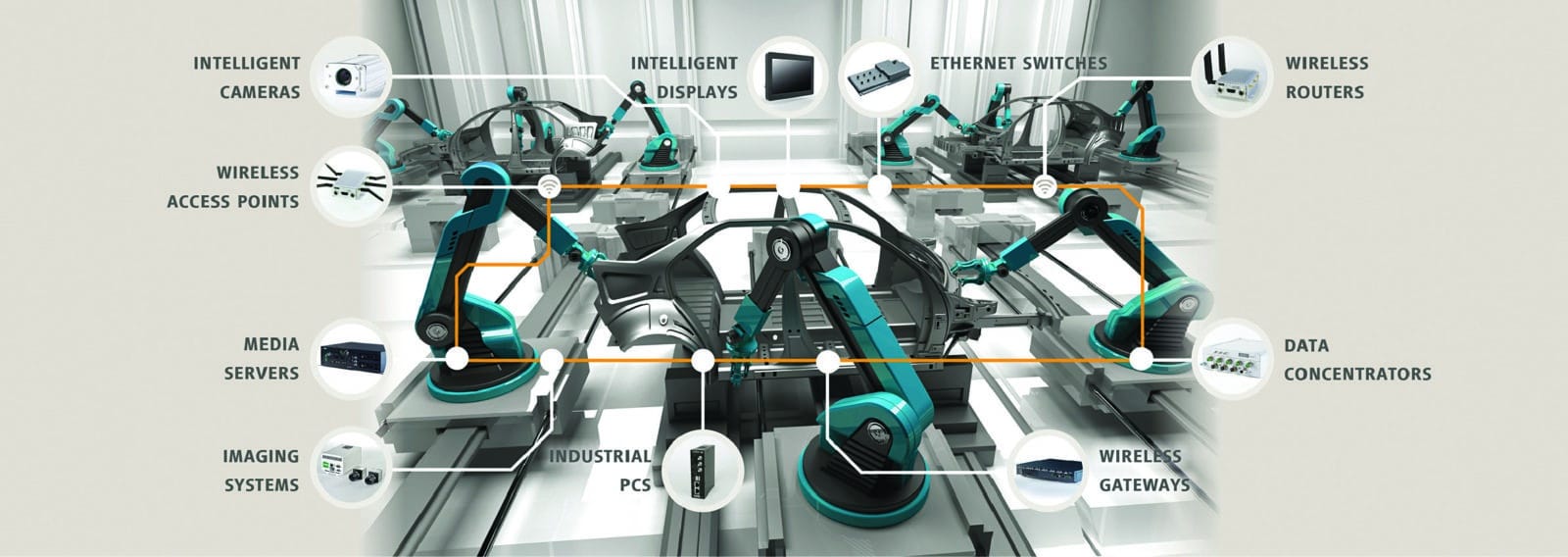
Experts believe that in future, with battery-managed electrical vehicles, the necessity to keep a check on foreign bodies, rough cuts and splits will increase. Enhanced efficiency, reliability, clarity and fast process are just some of the reasons to upgrade the imaging system not only in electrical vehicles but also in mobile communication networking as we move ahead to 5G technology.

DRAMs becoming smart
When we consider upgrades in IIoT implementation, DRAMs are a unique trendsetter.
Sivalenka states, “The 3D chip technology has converted to mainstream and for high capacity and performance, the industry is heading towards 3D DIMM RAM. The higher the bandwidth memory, the higher is the storage-on-chip and the wider the bus possible with off-chip memory.”
Smart networking protocols
ZigBee, Lora WAN, Ethernet protocol and Bluetooth 5.0 are some of the smart networking protocols that are implemented in smart lighting, smart energy and smart automation systems.
ZigBee Pro wireless network can support up to 2.4GHz band for the IoT. This flexibility and connectivity can be used in streetlight application. The wider the bandwidth, the greater the number of devices or lights that can be connected to each other in a long-range frame.
Due to the increasing bandwidth of networking protocols used in smart lighting, wireless technologies are also making way to high-end developments using Bluetooth, Wi-Fi and Li-Fi technologies. In the lighting field itself, the annual growth rate is anticipated up to 25 per cent.
Protocols coming up
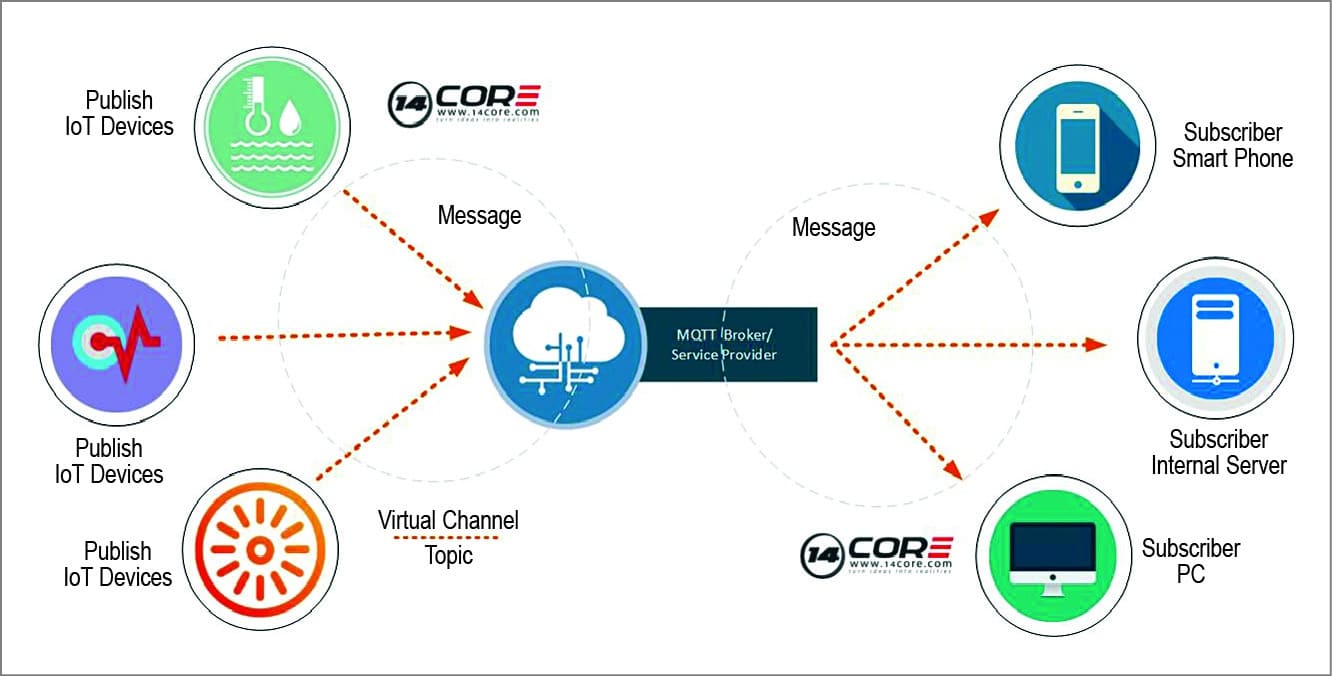
“Although companies have adopted protocols such as MQTT, Rest, MT-connect, object management group and OPC-UA, with the rising security concerns for connected devices there is an urgent need for establishing uniformly recognised global standards for both communication and security protocols,” shares Vinay Nathan, CEO, Altizon.
MQTT, short for ‘message queue telemetry transport,’ is an ISO standard designed for remote locations where the bandwidth is limited. This message protocol is used on top of TCP/IP protocol, to support wireless networks with varying levels of latency due to unreliable connections.
For instance, for measuring temperatures globally and creating a database where one can see the history, MQTT has a solution known as Wildcards. This solution can be used for any location (even customised areas), irrespective of the country.
When it comes to productivity, manufacturers can use open and free source standards to develop customised systems for their processes. Here, MT-connect protocol is a boon for the IIoT. It can be used to extract data from the controller and perform pattern recognition for monitoring the health condition of spindle and machine tool axes.
Object Management Group is helping with IIoT standardisation across the globe. Data Distribution Service (DDS), Systems Modeling Language (SysML) and Interaction Flow Modeling Language (IFML) are contributing to improve the productivity, cut costs and streamline processes of the IIoT.
IIoT no longer a hype
Earlier, the IIoT was an application that required lots of capital investment. So only up to 15 per cent of industrial assets was converted into digitised data. Now, as enterprises aim to lower sensor costs and change the route of sensor application, the IIoT is said to convert assets up to 35 per cent.
Initiatives have been taken in European countries like Germany and France to promote implementation of the IIoT on a big scale. Countries like USA, India and China are also deploying smart manufacturing technologies to increase their national GDPs. Schneider Electric has recently expanded its automation portfolio in India with the launch of IoT-enabled smart pumping solutions, which asserts that the IIoT is no longer a hype.
IIoT and smart applications
From smart dust to drones, futuristic farming to energy networks, motor control to machine-to-machine, IIoT applications are creating a web across the globe.
Motors are a generic element of the manufacturing industry. So their efficiency, reliability and power consumption need to be taken care of. FPGA ICs exhibit long-term reliability and long lifecycles, supporting the working of motors for long hours.
Similarly, there are devices that support the powerful Ethernet-based protocol for real-time communications.
5G is the latest trend, which has left 2G, 3G and 4G behind. This technology is evoking the interest of key industry players due to its higher bitrate, lower latency and extended bandwidth. For instance, smart cars and intelligent mobility systems largely depend upon 5G and the IoT. Smart cars provide sophisticated features such as infotainment, communications, diagnostics and driver assistance. Fully automated vehicles are still far off, yet some manufacturers are providing smart features like parking assistance and crash avoidance.
According to research reports, by year 2020, connected cars will account for up to 75 per cent of the worldwide shipments, which is quite large compared to the present scenario. And embedded systems will account for 40 per cent of the material cost of these complex vehicles.