COVID-19 is a pandemic that has caused crises and lockdown around the world. Such a lockdown had affected the business and services of many companies around the world. As many companies are dependent on humans and most of their products/services require human workers, the lockdown from COVID-19 had shut the doors of many companies around the country also. However, with the help of automation technologies like Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI), it could be possible to run the factories and services of a company during such a pandemic also.
Types of Automation:
Automation is a process of doing any work repeatedly without the need of any human and it can be done with the help of specialized software and hardware. The two main types of automation technology involves Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). In ML, the algorithm used for any kind of automation doesn’t require any programming but the machine is loaded with training data, which improves the performance based on the training environment/input. Such ML automation can make predictions and decisions without the user control. Such type of automation is used in financial market analysis, marketing, medical diagnosis, online advertising, telecommunication, banking and manufacturing.
AI on the other hand, is a kind of automation that refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think like humans and mimic their actions. Algorithms used for AI can mimic human intelligence and can make a machine to take decisions without the need of any human. That’s why AI can be a replacement for any human worker in many factories and business places. With the emergence of new software technologies like cloud computing and collaborative AI, the automation of many business processes can be done without the need of any human.
With the help of ML and AI, it’s possible to make use of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Internet of Things (IoT) and Cobots for automation. RPA is a kind of software robot that can automate any business process and can also work as a bot. Many companies use such RPA to automate their business products/services, either offline or online and eliminates the need of any human. RPA can be used as chatbots and companies are using it to provide online customer support also. IoT are devices that can be connected to any online cloud service and can be accessed remotely and can also be controlled/automated using ML/AI. For instance, an IoT 3D printer can be controlled by an AI cloud remotely, and other IoT devices like cameras and sensors can also be controlled like that. Cobots are collaborative robots and such robots can be in close proximity with humans and can interact with humans also. Unlike a traditional industrial robot, which works in an isolated environment, a Cobot can work with humans and is also safe for humans. However, there is no guarantee about the safety of a Cobot working with hazardous tools. For example, a Cobot working with welding and cutting tools can be harmful to humans but one that is only packing foam toys can be considered to be safe.
Restarting business using automation:
As the COVID-19 pandemic comes under control, many countries are unlocking and that includes India too. However, to boost-up the business and remain safe for any such future lockdowns, using automation for any business would be the right choice. Many companies have already used automation in the past, and companies like UiPath use automation technology to run BPOs without the need of any human. UiPath uses RPA for automation and can be useful for many companies. Most of the IT companies are already using their automation products for their business and there is a 20% growth since February 2020. In order to transform the traditional industry into fully automated one, it must comply with Industry 4.0 and that will require additional investments.
Investing in automation:
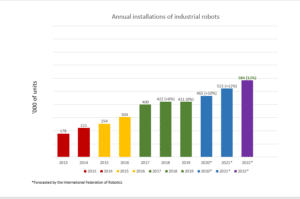
The global Industrial Automation Market size was valued at USD 157.04 Billion in 2018. It is expected to reach USD 296.70 Billion by 2026. The Indian Industrial Automation Market size was valued at USD 5 Billion in 2018. It is further expected to grow at a CAGR of 12% by 2023. Indian Industrial Automation Market is expected to reach $4.43 billion by 2023 and India ranks third worldwide in implementing robotic automation. As of 2018, there are overall 74 robot units per 10,000 employees globally. Companies like ABB have been providing automation products like robots to India already, and India needs to improve further. International companies like Siemens, ABB, GE, Endress+Hauser, Schneider Electric, Honeywell, Omron, Mitsubishi Electric, Rockwell, B&R Industrial Automation and IFM Electronic are the key players for providing automation products and services. However, Indian companies like Enpro Industrial Automation Pvt. Ltd., Larsen & Toubro, Titan Automation Solutions, SMEC Automation, Voltas and Adage Automation are also into such automation products and services. Therefore, investing in automation software and hardware can help improve the business after the COVID-19 lockdown and can assure a crisis-free business for the future.
 Transforming from traditional industry to Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0) can reduce industrial cost and improve the economy. Automation in any industry can help reduce production costs by roughly 25% – 40%. Interestingly, in the IT world, automation can cut business costs by up to 55% by introducing automation products like RPA and Cobots, as such highly effective automation can replace human workers. The increasing use of the IoT is referred to as Industry 4.0 at Bosch, and generally in Germany. Automation applications include machines that can predict failures and trigger maintenance processes autonomously, which can also eliminate humans. Over 20 years ago, outsourcing business processes hit a critical mass of acceptance and a line of uninterrupted growth began, and today — in India alone — the BPO industry is the country’s largest private sector employer, with a workforce of almost 3.5 million people. In 2014, Capgemini and UiPath began working on a RPA technology for BPO and came up with unattended automation, in which robots could manage robots and did not require any human control. In 2015, cost reductions exceeding 80% were seen and by the beginning of 2016, BPO providers were reacting to the new, disruptive proposition of these robots. Investing on Cobots can also improve the economy of a business because Cobots are easy to program and have user-friendly functionality. That also has short set-up time and can be configured easily without requiring any high cost training staff. Cobots can be used for different applications and they are highly flexible. They can give consistent results and can do repetitive tasks without any failure. Cobots can reduce human workload and prevent the workers from hazardous environments. As the cost of Cobots is less than any traditional industrial robot, it can also increase productivity and can potentially earn back the investment in as few as 200-300 days.
Transforming from traditional industry to Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0) can reduce industrial cost and improve the economy. Automation in any industry can help reduce production costs by roughly 25% – 40%. Interestingly, in the IT world, automation can cut business costs by up to 55% by introducing automation products like RPA and Cobots, as such highly effective automation can replace human workers. The increasing use of the IoT is referred to as Industry 4.0 at Bosch, and generally in Germany. Automation applications include machines that can predict failures and trigger maintenance processes autonomously, which can also eliminate humans. Over 20 years ago, outsourcing business processes hit a critical mass of acceptance and a line of uninterrupted growth began, and today — in India alone — the BPO industry is the country’s largest private sector employer, with a workforce of almost 3.5 million people. In 2014, Capgemini and UiPath began working on a RPA technology for BPO and came up with unattended automation, in which robots could manage robots and did not require any human control. In 2015, cost reductions exceeding 80% were seen and by the beginning of 2016, BPO providers were reacting to the new, disruptive proposition of these robots. Investing on Cobots can also improve the economy of a business because Cobots are easy to program and have user-friendly functionality. That also has short set-up time and can be configured easily without requiring any high cost training staff. Cobots can be used for different applications and they are highly flexible. They can give consistent results and can do repetitive tasks without any failure. Cobots can reduce human workload and prevent the workers from hazardous environments. As the cost of Cobots is less than any traditional industrial robot, it can also increase productivity and can potentially earn back the investment in as few as 200-300 days.
Made in China:
Most of the business products like smartphones, laptops and automobiles are manufactured in China because of the joint venture (JV) of many global companies with Chinese manufacturers. According to a report of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development 2003, China was the recipient of US$53.5 billion in direct foreign investment, making it the world’s largest recipient of direct foreign investment for the first time, to exceed the USA. Also, it approved the establishment of nearly 500,000 foreign-investment enterprises.
Companies with foreign partners can carry out manufacturing and sales operations in China, and can sell through their own sales network. Foreign-Sino companies have export rights which are not available to wholly Chinese companies, as China desires to import foreign technology by encouraging JVs and the latest technologies. Many electronic products are now manufactured in India but most of their semiconductor parts are imported from China, and without getting supplies from China, manufacturing of such products is not possible. Most of the Apple products are manufactured in China and after the lockdown of COVID-19, the manufacturing of Apple products has been disrupted. Foxconn, the Chinese contract manufacturer, is the top manufacturer of various branded products like iPhone, xbox360 and PlayStation for companies like Apple, Microsoft and Sony. Because of the safety concerns, Foxconn had shut down many of its manufacturing centres in China, since the lockdown. The microprocessor company, Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) had also suspended their manufacturing process, as it’s in JV with other Chinese partners too. Many software companies like Symantec are in JV with Huawei, forming Huawei Symantec Technologies Co. Ltd but the company is also affected due to the COVID-19 pandemic in China. Many automobile companies like Shanghai Automotive Industry Corporation of China are in JV with global companies like General Motors, Baojun, Buick, Chevrolet, Iveco, Škoda, and Volkswagen. Such companies have also suspended the manufacturing of their vehicles because of the lockdown, and many other car manufacturing companies are not able to manufacture because of not getting parts from China. In India also, manufacturing of many such products are suspended because of not getting parts from China. As China is the world’s top listed country for installing the highest number of Industrial robots, the manufacturing economy of China is better than the rest of the world. Because of this reason, manufacturers of China can produce high quality products at a better price and because of this reason many companies of the world have VJs with most of the manufacturers in China. However, boycotting Chinese products and services of China could impact the Indian companies who have dependencies on such Chinese manufacturers.
Industrial robots and Lights out manufacturing:
Industrial robots are the ultimate solution to automation and manufacturing of products economically. However, such robots are manufactured by only a few companies globally, and Japan is currently a top worldwide exporter of industrial robots. As indicated by the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), positions second on the planet by sales after China, revealing 45,566 units deployed in 2017.
Top 5 countries using industrial robots in 2018:
1. China — 154,000 industrial robots. China is responsible for 36% of total industrial robotics installations, with about 154,000 units.
2. Japan — 55,000 industrial robots.
3. U.S. — 40,300 industrial robots.
4. Republic of Korea — 38,000 industrial robots.
5. Germany — 27,000 industrial robots.
FANUC Robotics is the top leader in robotics and this Japanese company is supplying robots to many manufacturers around the world. Many US companies like General Electric and General Motors are in JV with FANUC and manufacturing industrial robots.
Industrial robots can automate a factory to manufacture the products but still requires some human operators. This could be a problem during any crisis like COVID-19, and such a factory can’t operate autonomously. However, light outs manufacturing can make it possible to run a factory autonomously with the help of AI and Cobots. In the Netherlands, Philips uses lights-out manufacturing to produce electric razors, with 128 robots made by Adept Technology. There are only nine human quality assurance workers who oversee the end of the manufacturing process. FANUC has been operating as a lights-out factory since 2001 and its robots are building other robots at a rate of about 50 per 24-hour shift and can run unsupervised for as long as 30 days at a time.
Therefore, it is possible to improve the business economy using automations like RPA, AI/ML, Cobots and lights out manufacturing. Such automation technology can keep any business process running during any crisis like COVID-19, and investing in such automation solutions is a better option.
By: Debojit Acharjee
The author is a software engineer and a writer