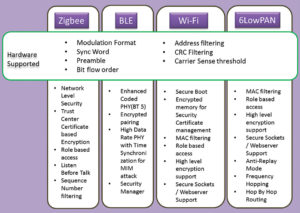
With protocols like Zigbee, security for specific end applications like smart meters and smart grid takes a very important place and hence is addressed in a very particular manner. The trust centre managing the encrypted keys that are negotiated between the coordinator and router in real time using the unique certificates issued by companies like Certicom, makes the link and network very secure.
Not to forget the recent release of BT SIG’s BT5 standard, which opens altogether different application avenues with precise focus on long-range and secured networks. Encoded PHY uses high data rate (up to 2Mbps) with variable spreading factor (1/2/4/8) to attain long range. The standard also enables long-range encrypted beacons for data exchange without entering a connection.
Many companies and developers intend to use the new BT5 physical layer for applications like tracking, location and access control. Enhanced beacon support feature of BT5 allows very quick packet exchange (including the user’s location and presence) to eliminate Man in the Middle attack.
Being plug-and-play in nature, Wi-Fi has become a prime focus of hackers nowadays. Every website having digital certificates authentication filters any remote IP attack or local machine malware attack by declining access to sites with unsigned certificates or the ones using lapsed/old certificates.
Especially nodes/sensors based on IP networks like 6LowPAN (using IPv6) or Wi-Fi have an edge over other proprietary ad-hoc network nodes. The uniqueness of IP address in each node, which is factory programmed and acts as a seed in obtaining the short address in the network, eliminates the replay attack or node shadowing.
Sensors using these communication standards commonly attract security attacks. But the effort of all developers and standard defining committees is commendable in making the wireless and wired networks secure enough to sustain.
Backhaul
Cloud or data centres require the highest level of security as these collate all kinds of data—whether it is your personal photos, banking passwords, IP or key to e-lock, or your company’s financial transactions, POS terminal’s certificates, etc. Hence it won’t be wrong to say that if there is a force of hackers which works day and night to intrude into these data centres, a bigger force works 24×7 to secure it too. Secured frameworks with digital security certificates, authenticated IP access and security-certified hosted domains exchanging data through documents signed with digital signatures are just some of the methodologies to have access authenticated and filtered at every single level every time.
In short
Security is one of the most crucial design requirements that needs to be considered before design development is initiated. Security in smart applications is a huge concern today. Along with opportunities, there are challenges as more and more devices join the IoT. It is important and essential to be vigilant on a personal level and ensure professionally that neither loopholes are left in an IoT-based system, nor shortcuts are strived for.