IaaS provides high-performance computing on supercomputers, computer grids or computer clusters. This helps solve complex problems involving millions of variables or calculations. Examples include earthquake and protein folding simulations, climate and weather predictions, financial modelling and product design evaluation.
Cloud computing is growing rapidly and involves potentially greater exposure to security threats and privacy breaches, especially when it comes to private and public cloud. It is a new way of providing computed resources and applications on-demand. It has become one of the most important research topics in computer science and information systems today.
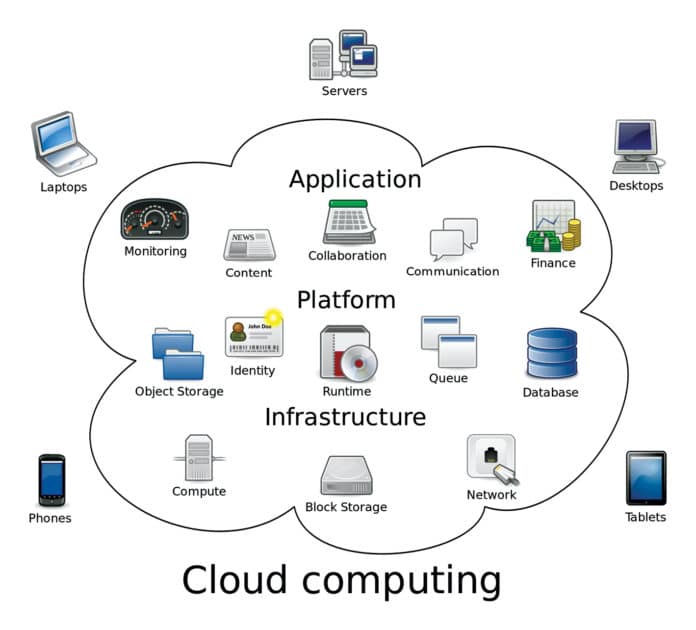
Three main categories of cloud computing are:
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Internet as a Service (IaaS)
[emaillocker] A form of cloud computing, IaaS provides virtualised computing resources over the Internet. It is a cloud model where units of computation, in the form of virtual machines and/or storage, are allocated to customers, who then access their assigned resources via wide area network (WAN). Cloud system consumers are granted complete control of all resources assigned to them, but they have no control over the positioning layer.
In an IaaS model, a cloud provider hosts infrastructure components traditionally in a data centre, which includes servers, storage, networking hardware, as well as virtualisation or hypervisor layer.
An IaaS provider also supplies a range of services to companies, including detailed billing, monitoring, log access, security, load balancing, clustering, backup, replication and recovery. IaaS provides greater level of automation and orchestration for important infrastructure tasks.
IaaS customers can access resources and services through WAN, such as the Internet. For example, they can log into the IaaS platform to create virtual machines. They can deploy middleware such as databases, create storage buckets for workloads and backups, and install enterprise workload into the virtual machines. Users can then use IaaS to track costs, monitor performance, balance network traffic, troubleshoot application issues, manage disaster recovery and so on.
Any cloud computing model requires participation from a provider, who is a third-party organisation specialised in IaaS. Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are independent IaaS providers. An enterprise may also opt for private cloud to become its own provider of infrastructure services.
AWS offers storage services such as Simple Storage Services (S3) and Glacier, as well as computer services such as its Elastic Compute Cloud (GCP). GCP offers storage and computer services through Google Compute Engine (GCE), as does Microsoft Azure.
There are many other smaller or niche players in the IaaS market, including Rackspace Managed Cloud, Century Link Cloud and Digital Ocean.
Benefits of IaaS
IaaS has a number of benefits, some of which are:
- Scalability. Resources are available as and when required by the customer and, hence, there are no delays in expanding capacity or wastage of any used capacity.
- Saves time and cost.
- Utility-based billing. The service can be accessed on demand and the user pays only for the resources that he or she uses.
- Location independence. The service can be accessed from anywhere using the Internet, so long as the security protocol of cloud allows it.
- More physical security.
- No single point of failure.
- Rapid innovation. Suppose an entrepreneur wants to launch a new product, the necessary computing infrastructure is readily available within hours in IaaS—it can sometimes takes months using other cloud platforms.
- Increases stability, reliability and supportability.
- Focuses on core business rather than IT infrastructure.
IaaS provides high-performance computing on supercomputers, computer grids or computer clusters. This helps solve complex problems involving millions of variables or calculations. Examples include earthquake and protein folding simulations, climate and weather predictions, financial modelling and product design evaluation.
Further, IaaS economically provides analysis of Big Data. Mining data sets (database includes cloud-based SQL and NOSQL) to locate or flush out hidden patterns requires huge amounts of processing power, which can be potentially done on an IaaS platform.
Running websites using IaaS can be less expensive than traditional Web hosting. IaaS provides features such as content delivery networks and load balancing. HP Enterprise Converged infrastructure also provides IaaS, and is a part of converged cloud solutions for public, private or hybrid cloud.
Technical challenges
According to a recent Forbes report, 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are being generated every day, and this is expected to multiply several times in the coming years. All the new technologies like machine learning and the Internet of Things (IoT) are fuelling data creation and, at the same time, increasing vulnerability to data breaches.
Well, the spectre of potential breaches is haunting both small and large businesses. Losing data can affect businesses very hard. For most medium- to large-scale businesses, experiencing a single hour of downtime can cost more than one million dollars. With such potential losses, it is no wonder that enterprises invest heavily in IaaS-based cloud systems.
While IaaS-based cloud computing brings many advantages, this model also raises significant technical security considerations and questions. Among these issues are operational trust modes, resource sharing of attack strategies and digital forensics.

Legal issues
In addition to the identified technical challenges, legal issues associated with IaaS-based cloud computing need to be analysed into a risk analysis plan. That way, potential consumers can make informed decisions about the appropriateness of utilising potential valuable resources. Some legal issues include consideration of jurisdictional problems, understanding and evaluation of cloud, stake-holders’ rights, and technical approaches to addressing the associated legal and jurisdictional issues.
IaaS is becoming extremely popular in mobile development, and this is especially the case with startups. It is being used to develop Web and mobile analytical tools, which are designed to oversee source code management, testing, tracking, payment gateways and so on.
System admins face numerous challenges today when it comes to managing IT infrastructure and data. Virtualisation software help them address these issues by making available virtual computer hardware platforms, virtual storage devices and virtual computer network resources. Virtual machines in a IaaS cloud system are helping make use of today’s high-powered hardware to the fullest.
Vinayak Ramachandra Adkoli is BE in industrial production. He was lecturer in mechanical department for ten years in three different polytechnics. Now, he is a freelance writer and cartoonist.
[/emaillocker]