Only 20 operators in 19 countries have deployed/launched both NB-IoT and LTE-M networks, according to the Global Mobile Suppliers Association.
The Global Mobile Suppliers Association (GSA) has released an update on the number of operators and countries supporting either or both Narrow Band IoT (NB-IoT) and LTE-M networks.
According to GSA, as of March 2019, 149 operators in 69 countries have invested in one or both of the NB-IoT and LTE-M network technologies.
About 102 operators in 52 countries have deployed/launched at least one of the NB-IoT or LTE-M technologies. Out of these, 20 operators in 19 countries have deployed/launched both NB-IoT and LTE-M networks.
Difference between NB-IoT and LTE-M networks
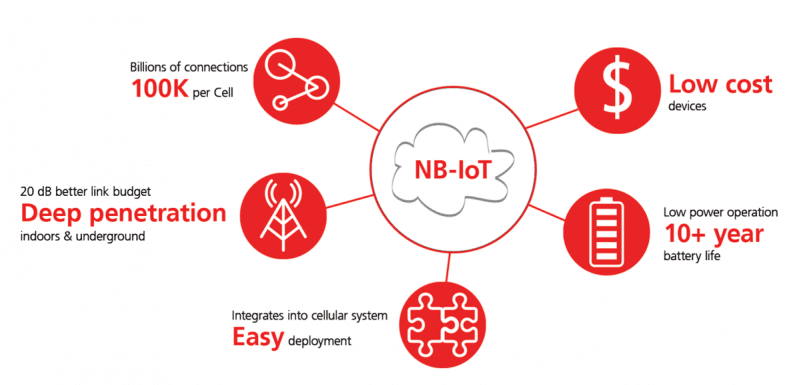
Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) is a Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) radio technology standard developed by 3GPP to enable a wide range of cellular devices and services.
NB-IoT focuses specifically on indoor coverage, low cost, long battery life and high connection density. NB-IoT uses a subset of the LTE standard but limits the bandwidth to a single narrow-band of 200kHz.1
LTE-M (LTE-MTC [Machine Type Communication]), which includes eMTC (enhanced Machine Type Communication), is a type of low power wide area network (LPWAN) radio technology standard developed by 3GPP to enable a wide range of cellular devices and services (specifically, for machine-to-machine and Internet of Things applications).
LTE-M is comparatively better than NB-IoT in terms of higher data rate, mobility and voice over the network. However, LTE-M requires more bandwidth, is costlier and cannot be put into guard band frequency band for now.
(With inputs from IoT Business News)